- Home
- Missions
- Data
- Communications
- People
- The Earth Observer Newsletter
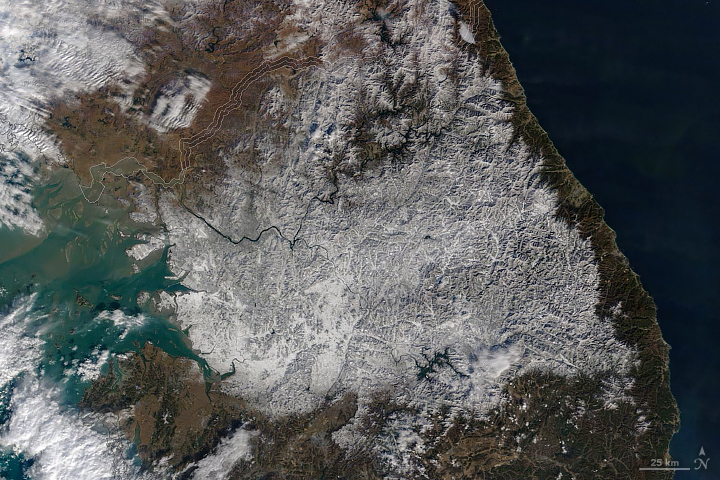

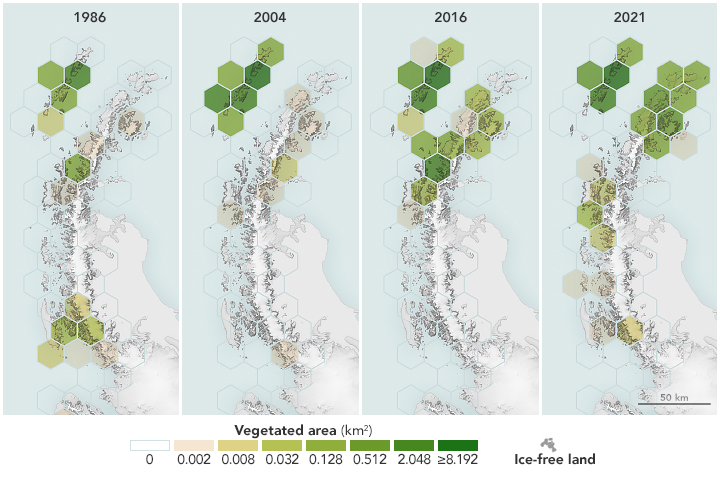
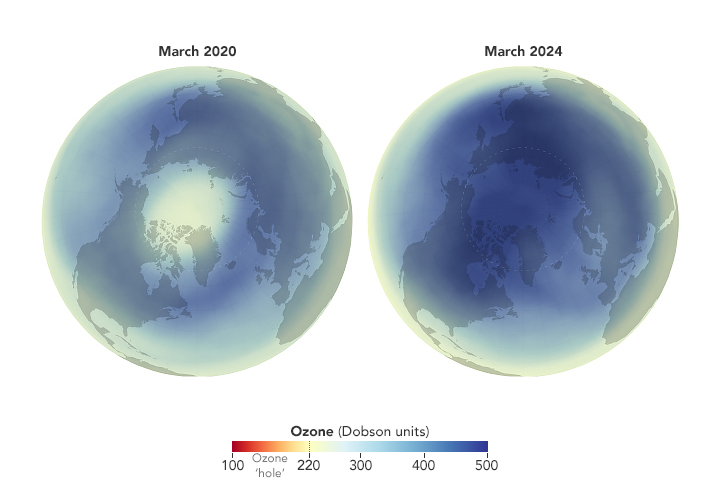
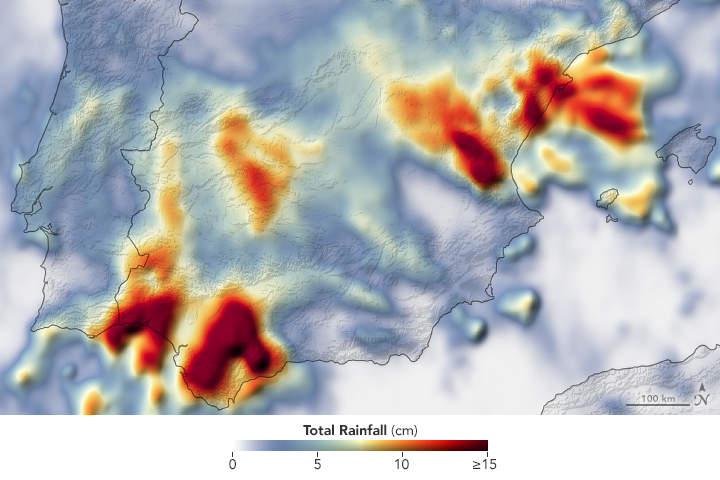
Recent Imagery
You will be directed to the NASA Visible Earth webpage when you select Images by Mission below, or click on the images at right that are randomly generated to represent four out of all possible topics.
You are here
Factsheets
NASA's Earth Observing System provides a variety of materials available for download. Feel free to choose a category below:
- Brochures
- Postcards
- Posters
- Science Writers’ Guide
- Mission Brochures
- Fact Sheets
- Calendars
- Booklets
- Lithographs
- Reference and Data Products Handbooks
- iBooks
- Activities
 |
Seadler 6.7.18 - ABoVE Infographic - FINAL Infographic 1 of 7 in a series for Jack Kaye and Bruce Tagg that show the value of airborne science to Earth science research. Each infographic covers a different airborne campaign and provides a few things we wouldn't have known without its aircraft data. This publication appears in: |
 |
Seadler 6.7.18 - SEAC4RS Infographic - FINAL Infographic 2 of 7 in a series for Jack Kaye and Bruce Tagg that show the value of airborne science to Earth science research. Each infographic covers a different airborne campaign and provides a few things we wouldn't have known without its aircraft data. This publication appears in: |
 |
Seadler - GRIP Results One-Pager NASA’s Genesis and Rapid Intensification Processes (GRIP) experiment studied the physical and environmental factors that contribute to hurricane formation and intensification. The experiment sought to answer 1) What environmental and inner-core processes determine whether a storm will strengthen into a hurricane? And 2) To what extent can we predict whether this intensification will occur? From 15 August through 30 September 2010, NASA flew three aircraft carrying fifteen instruments over the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Mexico to measure vertical and horizontal wind speeds, precipitation, pressure, temperature, and humidity in and around tropical cyclones in an attempt to figure out what fuels the powerful storms. This publication appears in: |
 |
Seadler - GRIP Results Slide The Genesis and Rapid Intensification Processes (GRIP) campaign studied the physical and environmental processes that affect the lifecycle of Atlantic hurricanes from formation to dissipation. This publication appears in: |
 |
Seadler - SABOR Results One-Pager NASA’s Ship-Aircraft Bio-Optical Research (SABOR) experiment used cutting-edge technology in the air and the sea to verify and measure the amount, type, and distribution of phytoplankton in different ocean environments. The field campaign sought to answer whether new technologies, such as lidar and polarization, could be used to better observe changes in oceanic ecosystems. From 17 July to 17 August 2014, the SABOR campaign took in situ, ship-based above-water, and airborne measurements of phytoplankton content, particulate matter, and oceanic optical properties. The campaign sought to cover a broad range of oceanic environments—from optically complex coastal waters to clear blue open ocean—for maximum accuracy. This publication appears in: |
 |
Seadler - SABOR Results Slide The Ship-Aircraft Bio-Optical Research (SABOR) experiment used cutting edge technology in the air and the sea to verify and measure the amount and distribution of phytoplankton in different ocean environments. This publication appears in: |
 |
Seadler - SEAC4RS Results One-Pager NASA’S Studies of Emissions and Atmospheric Composition, Clouds, and Climate Coupling by Regional Surveys (SEAC4RS) campaign studied how aerosols are injected into and influence upper tropospheric and lower stratospheric composition and chemistry. The campaign sought to answer: − How does deep convection distribute aerosol particles and gases, including pollutants, in the atmosphere? − How do gases and aerosols influence atmospheric chemistry and climate? During multiple regional flights across the southeastern and southwestern United States, NASA incorporated measurements from satellites, research aircraft, weather balloons, and ground sites to measure atmospheric convection, composition, and chemistry. In particular, SEAC4RS examined the role of pollution, large urban centers, agricultural fires, and areas of intense isoprene emissions in the southeastern United States, as well as wildfires and the North American monsoon in the southwestern United States. This publication appears in: |
 |
Seadler - SEAC4RS Results Slide The Studies of Emissions and Atmospheric Composition, Clouds, and Climate Coupling by Regional Surveys (SEAC4RS) campaign studied how aerosols are injected into and influence upper tropospheric (UT) and lower stratospheric (LS) composition and chemistry. This publication appears in: |
