- Home
- Missions
- Data
- Communications
- People
- The Earth Observer Newsletter
Recent Imagery
You will be directed to the NASA Visible Earth webpage when you select Images by Mission below, or click on the images at right that are randomly generated to represent four out of all possible topics.
You are here
Science Communication Material
NASA's Earth Observing System provides a variety of materials available for download. Feel free to choose a category below:
- Brochures
- Postcards
- Posters
- Science Writers’ Guide
- Mission Brochures
- Fact Sheets
- Calendars
- Booklets
- Lithographs
- Reference and Data Products Handbooks
- iBooks
- Activities
 |
Aqua The launch of NASA’s Aqua spacecraft continued the Earth Observing System (EOS) series of comprehensive satellites to monitor the Earth from a space-based platform. Aqua was so named because it obtains significant information about water in the Earth system including ocean surface water, humidity, precipitation infiltration, and runoff. Data from six Aqua instruments provide continuous, long-term records of the hydrologic cycle around the world, which are combined with data from other Earth-monitoring satellites launched by NASA and other countries. This is related to the following mission(s): This publication appears in: |
 |
Gravity Recovery And Climate Experiment (GRACE) While gravity is much weaker than other basic forces in nature, such as magnetism and electricity, its effects are ubiquitous and dramatic. Gravity controls everything from the motion of the ocean tides to the expansion of the entire Universe. To learn more about the mysteries of gravity, twin satellites named GRACE, short for the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment, are being used to make detailed measurements of Earth’s gravity field. This is related to the following mission(s): This publication appears in: |
 |
ICESat The primary goal of ICESat is to quantify ice sheet mass balance and understand how changes in the Earth’s atmosphere and climate affect the polar ice masses and global sea level. ICESat also measures global distributions of clouds and aerosols for studies of their effects on atmospheric processes and global change, as well as land topography, sea ice, and vegetation cover. This is related to the following mission(s): This publication appears in: |
 |
Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) The first EOS satellite, called Terra, was launched on December 18, 1999, carrying five remote sensors. The most comprehensive EOS sensor is MODIS, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer. MODIS offers a unique combination of features: it detects a wide spectral range of electromagnetic energy; it takes measurements at three spatial resolutions (levels of detail); it takes measurements all day, every day; and it has a wide field of view. This is related to the following mission(s): This publication appears in: |
 |
MODIS Monitoring Sea Surface Temperature, Chlorophyll Concentration, and Phytosynthetic Activity A sensor orbiting the Earth aboard NASA’s Terra and Aqua satellites is now collecting the most detailed measurements ever made of the ocean’s surface environment. Like a sophisticated thermometer in space, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) can measure sea surface temperature every day over the entire globe. This publication appears in: |
 |
SORCE SORCE, launched in March 2003, aims to enable solar-terrestrial studies by providing precise daily measurements of the Total Solar Irradiance and the Spectral Solar Irradiance at wavelengths extending from the ultraviolet to the near infrared. This is related to the following mission(s): This publication appears in: |
 |
The Gravity Recovery And Climate Experiment (GRACE) To learn more about the mysteries of gravity, twin satellites named GRACE—short for the Gravity Recovery And Climate Experiment—were launched to make detailed measurements of Earth’s gravity field. This experiment could lead to discoveries about gravity and Earth’s natural systems, which could have far-reaching benefits to society and the world’s population. This is related to the following mission(s): This publication appears in: |
 |
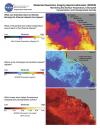
Urban Growth These images show the extent of land developed as urban, commercial and residential areas between 1986 and 2000, and projected development to 2030 in the Baltimore-Washington D.C. Metropolitan area. Past and current urban extent were derived using Landsat Thematic Mapper (TM) and Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) satellite images. This publication appears in: |
 |
AIRS/AMSU/HSB The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS), together with the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit (AMSU) and the Humidity Sounder for Brazil (HSB) (Note: The HSB instrument failed after reaching orbit.) on the Aqua mission, represents the most advanced sounding system ever deployed in space. The system is capable of measuring the atmospheric temperature in the troposphere with radiosonde accuracies of 1 K over 1 km-thick layers under both clear and cloudy conditions, while the accuracy of the derived moisture profiles exceed that obtained by radiosondes. This is related to the following mission(s): This publication appears in: |
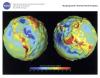 |
GRACE This lithograph displays the most accurate map to date of Earth’s long wavelength gravity field and is the first version to be released by NASA’s Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) mission. We call these maps gravity anomaly maps because they show us how much Earth’s actual gravity field departs from "normal," as defined by a simplified mathematical gravity model that assumes the Earth is perfectly smooth and featureless. The maps reveal that the Earth is a restless, dynamic planet, both at its surface and deep within its interior. This is related to the following mission(s): This publication appears in: |
